2500+
Successful Projects

It’s 2025, and we are almost at 1/4 of the 21st century. The technology has started to untangle itself—your alarm starts to ring automatically after you complete 8 hours of sleep, your room’s lights switch on as you wake up, and your car syncs with your morning schedule. This is just a teaser of what we could expect from the IoT technology. IoT-enabled mobile apps are revolutionizing everyday life in 2025, and the trend shows no sign of slowing down.
So, why has IoT mobile app development become so crucial today? The answer lies in the fact that most of the smart devices we use, whether smartphones, voice assistants, wearables, etc., are commanded and monitored by IoT-enabled mobile apps. In simple words, IoT apps let us control all interconnected things with just a tap.
Table of Contents
You will be surprised to know the latest statistics regarding the increasing market value of IoT (Internet of Things) devices, which is expected to increase from $15.14 billion in 2023 to $29.42 billion by 2030. With that being said, the demand for IoT-enabled mobile apps will increase progressively.
But let’s not jump too far! Let’s examine the influence of IoT-enabled mobile apps and their use cases. The ultimate goal of this guide is to help you understand the crucial role of IoT-enabled mobile apps in everyday life and the future trends of IoT applications that could positively affect our lives.
IoT-enabled mobile apps serve as a bridge between users and IoT devices. These apps allow individuals to monitor, manage, and interact with smart devices. As IoT devices rely on software for control and communication, these mobile apps play a crucial role in enabling seamless connectivity and enhancing user experience.
These apps empower users to control smart devices, from adjusting home settings to managing logistics and healthcare applications. With the increasing adoption of IoT devices, the demand for such apps is expected to rise significantly in the coming years.
With global spending on IoT reaching an impressive $805.7 billion in 2025, the world is witnessing a paradigm shift. But what's driving this surge, and how are businesses and manufacturers capitalizing on this trend? Well! The numbers don't lie. By 2026, the IoT ecosystem is projected to surpass the trillion-dollar mark, fueled by relentless innovation and strategic investments in the field.

As billions use smartphones worldwide, these pocket-sized powerhouses have become the primary gateway to the IoT universe. Whether you're adjusting home lighting or monitoring a factory's temperature, mobile apps seamlessly connect us to our smart devices, making management intuitive and efficient.
The global adoption of IOt-enabled mobile apps continues to soar, with each passing day adding to the user base. As a result, mobile apps have become the go-to interface for interacting with IoT devices. These apps don't merely supplement the use of IoT; they enhance it. These apps make IoT systems work more intelligently and responsively by optimizing device interactions, automating tasks, and providing actionable insights.
As we look ahead, the mobile IoT app market will continue to thrive. Expect innovations like augmented reality (AR) overlays for real-time device visualization, predictive maintenance algorithms, and personalized user experiences.
The impact of IoT technology on mobile app development has been positive so far. It has streamlined the development process, allowing developers to add user-friendly features. IoT has opened up new opportunities for modern and inter-connected mobile app development to offer users seamless experiences.
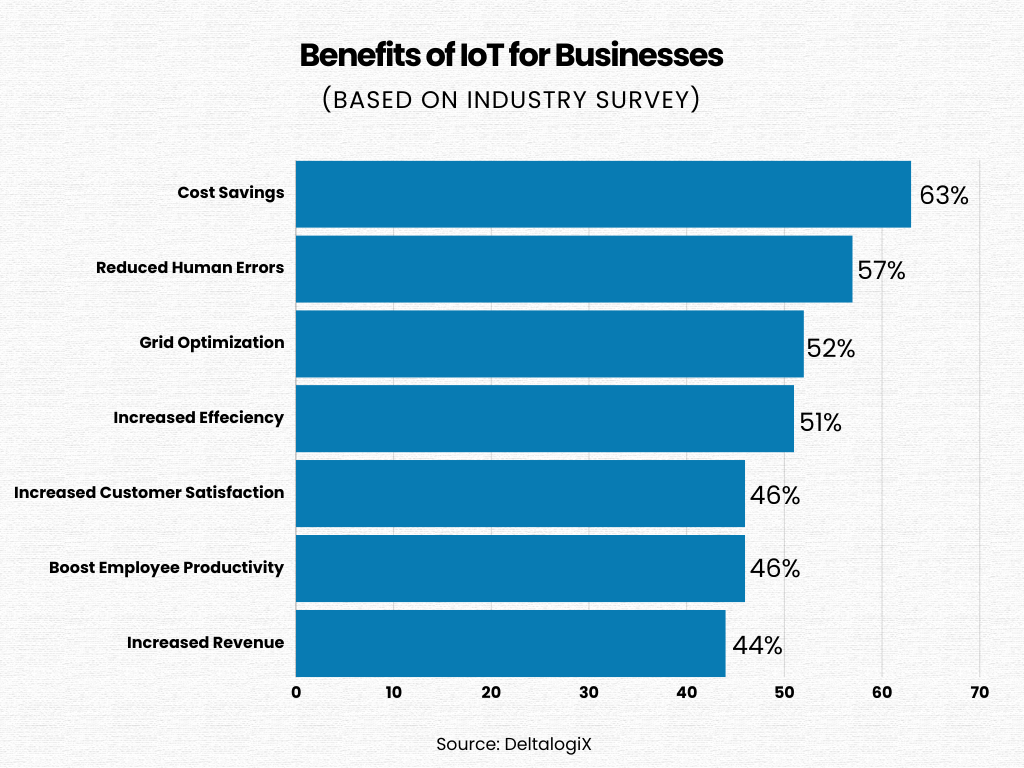
The Internet of Things (IoT) necessitates the development of mobile apps that can function across a variety of platforms and devices. This need has broadened the horizon for hybrid applications, which have seen significant enhancements since the emergence of IoT.
Advances in User Experience (UX) and coding techniques have allowed these hybrid applications to deliver top-notch performance across all interconnected devices and platforms. As a result, we now have distinctive, feature-packed mobile applications capable of performing multiple tasks at once.
In IoT mobile app development, connectivity options extend beyond the conventional ones, such as cellular, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth. These mobile applications can set up connections with smart devices and integrate with gateways using technologies like Near Field Communication (NFC), Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID), Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), and other IoT-specific protocols.
IoT promotes interaction among connected devices, leading to the automatic incorporation of device features into the IoT application. This aids developers in crafting superior functionalities and enhanced features for mobile IoT applications while exerting the same effort they would for non-IoT mobile apps.
Mobile apps for IoT-based solutions are required to analyze collected data in real time and offer insights. This has led to the increased integration of technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) in the development of mobile apps for IoT.
In an IoT environment where devices are connected via operating systems and connection protocols, data security is a significant concern. However, IoT-based applications prioritize security above all else, ensuring the prevention of glitches and security issues for the data collected from connected devices.
Technological advancements in IoT and its integration with emerging technologies like AI and ML have led to the development of innovative solutions that hold the potential to overcome real-world challenges in different industries and sectors.
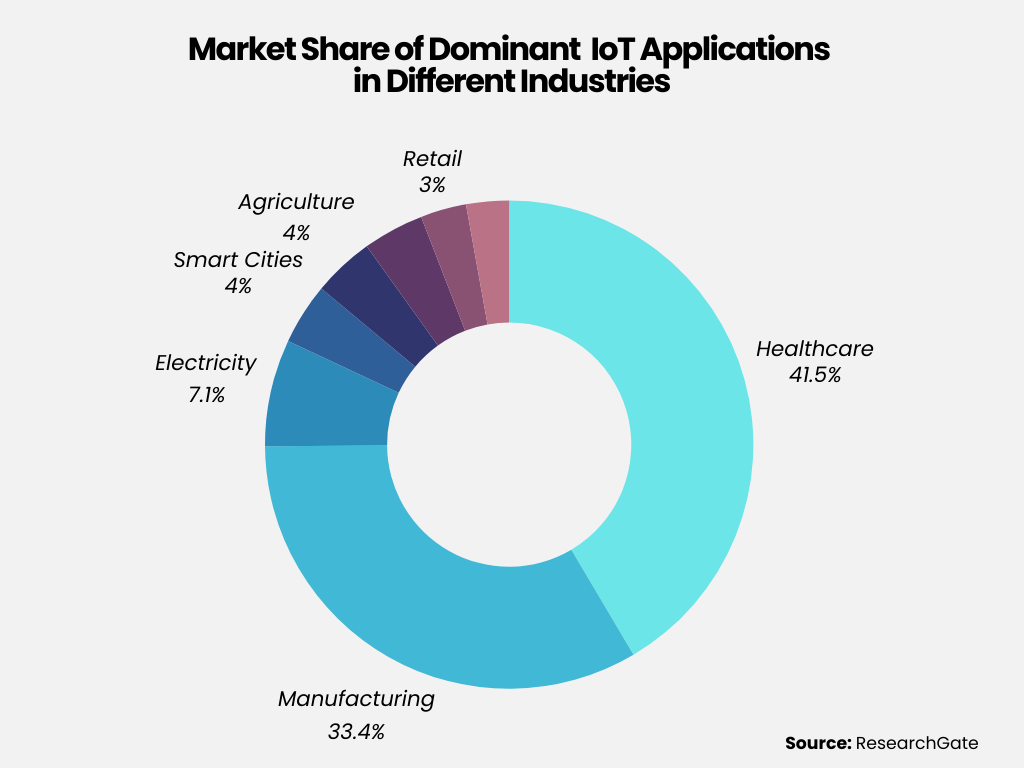
Here, we have listed 9 real-life use cases of IoT-enabled mobile apps that are already affecting our everyday lives.
The best Internet of Things (IoT) technology can do is transform cities into more efficient and livable spaces, revolutionizing their operation and development. By leveraging IoT technology, urban areas can manage traffic, modernize public services, minimize waste, and enhance resource efficiency through service automation. This technology can also stimulate economic growth and aid in the transition to a greener city.
For instance, Barcelona has started deploying intelligent streetlights fitted with sensors, leading to energy conservation. These lights modulate their intensity based on traffic flow, thereby conserving energy while ensuring adequate lighting.
Similarly, Singapore's Smart Nation program employs a sensor and camera network to monitor street cleanliness and crowd density, enabling more proactive city service management.
A scalable IoT app framework that can accommodate a city's expanding needs and intricacies facilitates the growth of smart cities. This framework allows for the establishment of a unified network of critical systems capable of addressing dynamic urban issues and adapting to the requirements of its residents.
Here are some real-world IoT applications for Smart Cities:
Insurance companies are among the early adopters of IoT technology. They use real-time data from IoT-enabled mobile apps to tailor policies, proactively manage risks, and elevate customer experiences. These apps enable insurers to understand, anticipate, and cater to individual requirements.
For instance, Progressive Insurance's Snapshot program uses a plug-in gadget to monitor driving patterns, such as speed, braking, and duration. By analyzing IoT data on personal driving behaviors, insurers can propose customized premiums and incentivize safe drivers with more favorable rates.
The health and life insurance sectors are also adopting IoT mobile app innovations. For example, John Hancock, a top-tier insurance company, has introduced a program that monitors physical activities. Policyholders who achieve specific fitness targets can receive discounts and rewards, encouraging them to lead a healthier lifestyle.
IoT mobile apps are also making a substantial difference in home insurance. Smart home gadgets that identify leaks, smoke, or unauthorized access can be linked with insurance policies to provide extra coverage. This allows insurers to lessen risks, decrease claims, and boost customer satisfaction.
Here are some real-world examples of IoT-enabled mobile apps in insurance:
The Internet of Things (IoT), particularly the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT), has been a breakthrough technological advancement in the healthcare sector. IoT-enabled mobile apps are empowering healthcare providers to deliver personalized care. These applications enable real-time monitoring of vital signs, chronic diseases, and overall patient health, facilitating prompt responses to significant changes in patient health and simplifying the management of chronic diseases.
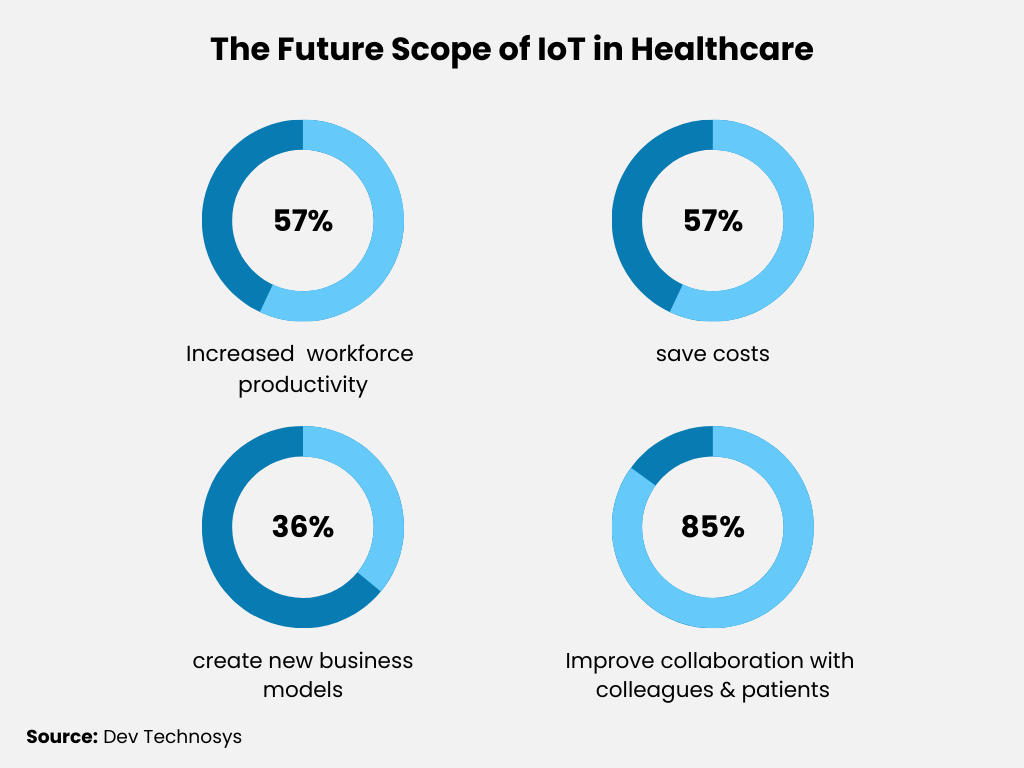
One of the most prevalent applications of IoT in healthcare is remote patient monitoring systems. For instance, telemedicine app development companies use mobile apps to continuously track health conditions and automatically relay this data to healthcare professionals. This immediate access to data allows healthcare providers to respond swiftly to patient health changes and modify treatment plans as needed.
Another area where IoT is making significant progress is medication management. Smart device applications, such as pill dispensers, remind patients about the correct dosages and alert caregivers if a dose is skipped. These solutions boost compliance with medication schedules and enhance overall patient health.
Health institutions are also reaping the benefits of IoT applications. They use these apps to monitor medical equipment, track assets and even oversee hygiene compliance. With such deep insights, hospitals can timely repair or replace equipment, optimize operations, and cut costs while fostering a safer healthcare environment.
Here are some real-world examples of IoT applications in healthcare:
IoT-enabled mobile apps are beneficial not just for cities but also for countryside farmers. These apps streamline labor-intensive tasks and make data-driven crop harvesting, fertilization, and watering decisions. They can also provide valuable insights into soil health, moisture content, and machinery performance. This information is crucial in preventing resource wastage, enhancing crop yield, and boosting operational efficiency.

When it comes to indoor farming, IoT enables the tracking and control of micro-climate conditions, leading to improved production and quality assurance. In the case of outdoor farming, IoT aids in the development of intelligent irrigation and fertilization systems. There exist sprinkler systems, for example, that release water only when necessary, fostering sustainable resource usage.
The concept of smart farming also encompasses livestock management. This assists farmers in early disease detection, efficient feed management, and accurate prediction of optimal breeding times. It's a degree of oversight that was previously unthinkable.
Here are some real-world examples of IoT applications in agriculture:
Today, the logistics sector is experiencing a surge in the use of IoT apps and devices that provide unparalleled visibility and automation. These tools are gaining popularity due to their ability to track shipments and vehicles in real time, predict maintenance needs, reduce costs, and select the most efficient routes.
The focus of emerging IoT app development is also shifting towards fleet management. Companies like UPS are integrating sensors into their vehicles to keep an eye on their condition, driver behavior, and fuel efficiency.
The data gathered from these sensors aids in proactive maintenance, promotes safer driving habits, and enhances overall operational efficiency. Adopting innovative IoT app deployment strategies can help you leverage these advancements and boost your profitability.
Here are some real-world applications of IoT in Logistics and Transportation:
Internet of Things (IoT) technology has greatly influenced the retail industry. The power of interconnected devices can be leveraged to enhance various aspects of retail operations, such as refining inventory management, streamlining supply chain processes, minimizing waste, and promoting sustainability.

Furthermore, IoT applications are transforming conventional shopping experiences into personalized, interactive adventures. For instance, many shopping stores in Miami have started offering customers tablets that enable customers to explore products, reserve fitting rooms, and even adjust the fitting room lighting to mimic different times of the day.
In addition, Amazon Go's cashier-free stores have done away with the need for traditional checkout queues. Customers simply enter the store, select their items, and leave, with the total cost automatically debited from their Amazon account. This seamless shopping experience is made possible by a combination of IoT sensors, computer vision, and advanced machine learning algorithms.
Moreover, IoT applications allow retailers to track customer shopping behaviors such as purchase history, preferences, and location data, enabling them to tailor experiences that align with individual customer needs.
Here are some real-world examples of IoT applications in retail:
While hospitality remains one of the slowest adopters of IoT technology, it still holds the potential to revolutionize the industry by automating mundane tasks and interactions. This allows staff to concentrate on more pressing matters, thereby enhancing the guest experience.
For instance, many international hotels have started embracing Digital Key technology. This IoT-enabled application allows guests to skip the front desk, choose their room, and unlock the door using their smartphones.
Furthermore, a mobile app lets guests manipulate room features such as temperature, lighting, and entertainment systems. This provides added convenience for guests, streamlines hotel operations, and optimizes energy consumption based on the data collected.
Marriott International is also exploring the use of IoT to provide a more comfortable and highly personalized guest experience. Their mobile app enables guests to adjust room temperature, lighting, and other features to their liking.
The restaurant industry is also adopting IoT apps. For instance, smart refrigerators can monitor temperature and humidity levels, helping to keep food fresh and reduce waste.
Here are some real-world examples of IoT applications in the hospitality sector:
These advancements not only enhance the guest experience but also improve operational efficiency and sustainability in the hospitality sector.
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) has been groundbreaking for the manufacturing sector. It enables factories to leverage connected devices to tap into the potential of data. By linking machinery and factory components to sensors, a network is established that allows for real-time analytics.

This forms the foundation for strategic decision-making and operational efficiency. The outcome is a reduction in energy use, improved asset monitoring, and early identification of machinery problems.
For instance, the Siemens' Amberg Electronics Plant in Germany has achieved 75% automation through IoT mobile app solutions. Sensors affixed to factory machinery constantly oversee the production line, pinpointing bottlenecks and minimizing waste. These sensors ensure smooth operations, monitor machine performance, forecast maintenance requirements, and avert expensive malfunctions.
However, the IoT's influence extends beyond the factory floor. RFID tags and GPS technology offer a comprehensive view of the entire supply chain, from the inception of a product to its delivery, guaranteeing transparency and responsibility.
Here are some real-world examples of IoT applications in manufacturing:
Smart Grids are more advanced and high-tech electrical systems that supply power directly to homes and industries. The IoT-enabled Smart Grid systems use digital technologies to monitor and control the electricity flow from power plants to homes. The enhanced IoT technology is behind the smart grid’s reliability, improved power distribution, and reduced energy waste.
For instance, many US states, including Tennessee, have implemented IoT-enabled smart grids that have greatly reduced energy outages. The systems allow the state’s Electric Power Board to keep track of electricity infrastructure in real-time, resulting in quick responses to power outages and customer complaints.
Inspired by Tenessee, Bornholm, an island in Denmark, has been testing smart grid systems to integrate renewable energy resources into usable power sources. At the same time, IoT-enabled mobile apps let consumers monitor how much energy is being used, making it more efficient and environment-friendly.
Real-life Applications of IoT in Smart Grids:
IoT mobile apps and their use cases have already been impacting various sectors and industries. Additionally, the influence of IoT technology on mobile app development is above everything. Technology has helped businesses create an interconnected environment where everything can be controlled over mobile apps without the hassle of even getting out of bed.
The potential of IoT-enabled mobile apps is countless, and having understood its concept will help you a lot in leveraging the powers of this advanced technology. As we conclude this guide, we hope all your questions and queries regarding IoT technology have been solved to a great extent. For any inquiry or help with the IoT app development, you can contact Mtoag Technologies anytime. Our IoT experts would love to connect with you.
A common use case of IoT is remote asset monitoring. Companies can use IoT devices to monitor the condition and location of their assets in real-time.
IoT has wide applications in various sectors, such as smart agriculture, smart homes, healthcare, smart cities, and wearables.
IoT devices are often controlled and monitored through dedicated mobile apps. Google Nest and MyFitnessPal are examples of such apps.
IoT in mobile app development enables enhanced hybrid app development, which allows developers to create apps that run on multiple platforms and devices.
The four types of IoT applications include Consumer IoT (e.g., wearables), Commercial IoT (e.g., healthcare and transport industries), Military Things (IoT in the military field), and Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT, e.g., manufacturing and energy sectors).