2500+
Successful Projects

The term "fintech" stands for financial technology.
FinTech is one kind of software or mobile application that helps enhance and automate conventional financing methods for companies.
FinTech software uses the newest technology to manage business operations and expedite conventional financial transactions for businesses and customers.
It is an all-encompassing word that covers all financial technology, from banks to capital markets like investment businesses, hedge funds, and credit card corporations. The fintech sector includes everything from payment methods and banking facilities to online insurance and lending markets and even financial software.
Fintech is a rapidly expanding sector that assists businesses in exploring opportunities for increased productivity, cost savings, innovation, and risk management. Fintech services from a fintech software development business are essential to remain on top.
It alludes to the formation of a market where new technology use cases are developed and implemented to make more straightforward, more traditional financial processes. Are you intrigued by it? Are you keen on learning more about the newest fintech trends to look out for? Could you read our blog to get the whole scoop?
The Fintech industry has also seen rapid expansion in recent years and is predicted to generate $158 million in revenue by 2023, which bodes well for its future.
Now that you have a fundamental knowledge of fintech solutions let's examine some specific instances to understand them better.
We cannot deny the significant impact fintech firms have had on how people and businesses purchase and sell goods. Money transfers via smart devices were once fiction but are now a reality. Nowadays, most consumers prefer to pay their bills online, no matter what. Online transactions have made it such that the cash world has been doomed.
Trading
Trade and investing have taken over people's lives in the twenty-first century. It is a definite thing and among the safest techniques to increase your financial resources over time. As previously indicated, trading is one of the safest strategies to generate fast money. Either stock and bond trades or foreign currency transactions may be used to accomplish it.
Today, trading is a relatively straightforward activity because of fintech technology consultancy. Online platforms created expressly for this purpose are now available. Even though online trade has been around for a few years, it is growing in popularity daily. Computer-based platforms and mobile/intelligent/electronic devices may be used to complete the task. Additionally, you will see several stock trading applications where you may manage your assets well and carry out trades quickly. In this situation, a fintech startup can assist you in getting started.
The Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies
The list of fintech examples would be lacking without including cryptocurrency and blockchain. To reduce fraud or defective transactions and safeguard financial data on blockchain technology, buying or selling bitcoins has become the norm.
These are some examples of fintech. Fintech refers to various financial operations, including money transfers, checking a cheque at the bank using a smartphone, generating capital for new businesses, and managing all of your assets without needing a financial advisor.
How Fintech Promotes Economic Development?
The fintech ecosystem is a developing organization with economic origins. The entire structure aids in accelerating economic growth and expanding employment prospects. A financial software development business can assist you in getting started with fintech, which has, according to many studies, made a significant financial contribution to innovation and financial inclusion. Millions of individuals, especially those living in poverty in developing economies, have seen increased income. By enabling new digital technologies and methods, fintech also helps economic growth. It has made transactions more straightforward and made it easier to acquire digital data, which has created job prospects.
Fintech is a young sector focusing on leveraging technology to provide financial services. This study area includes a wide range of operations, such as the online transfer of assets, making payments, and making investments. Between service providers and customers, the financial ecosystem serves as a conduit. As a result, it offers a platform for financial industry innovation. It has improved financial inclusion by bridging the divide between technology and financial services business models.
The financial services sector is changing because of fintech. It is best described as disrupting conventional banking and finance paradigms with new ideas and technology that enable consumers to manage their money more effectively and save time. A well-known financial software development company invests significantly in discovery, creation, and innovation. Every project we work on 0is approached from a long-term perspective. We understand the Fintech industry and have created solutions for top financial sectors, including banking, the stock market, the investment industry, etc., thanks to our ability to provide companies with peace of mind utilizing cutting-edge software.
Fintech's importance
Businesses no longer limit themselves to conventional methods due to technology improvements; credit goes to the fintech revolution and fintech solutions!
Companies are developing cutting-edge strategies to accomplish their objectives with the assistance of a fintech consultant as technological maturity is at an all-time high. One of them also consists of financial solutions. It is a process wherein advancements in banking. Insurance and other financial services sector have given rise to new technologies that have made it feasible for customers to trade with businesses more affordably, quickly, and effectively. It is a revolution that introduces new services and goods to alter how things operate. You may depend on financial technology consultancy for extra assistance with this.
Integrating technology into conventional financial operations, fintech, or financial technology, revolutionizes the financial services sector. As a result, both firms and consumers now have new possibilities.
Here are a few examples of how fintech is altering conventional financial services:
Digital Payments
Through mobile wallets, contactless payments, and peer-to-peer transfers, fintech has made it simpler and more accessible for customers to make digital payments. As a result, traditional banking services and real currency transactions have become less necessary.
Online Lending
Fintech firms use technology to provide consumers and businesses with fast and straightforward access to loans. This has hampered the lengthy and sluggish conventional financing procedure.
Robo-Advisors
Using robo-advisors, fintech has made it feasible to automate portfolio management and financial advice. Consumers may now invest more quickly and affordably thanks to this.
Overall, fintech is upending conventional financial services by giving customers, and companies access to more effective, inexpensive, and accessible alternatives.
Read More: How Fintech changed the way SME sector conducts business
In this blog, you will find information about fintech on different issues.
Topic 1: You will read the Definition and how it has grown in recent years that become popular among the people. Also, many need to learn why it is essential to know about it and to work with this industry in the coming years.
Topic 2: The growth of the fintech industry: In this part, you will learn about the historical evolution until 2023. Moreover, you will discover the newest trends and growth projects in the coming years. Lastly, know the key drivers that help the fintech industry grow in various forms.
Topic 3: Technology in Fintech Industry: In this post, learn about the role of technology that fits the fintech industry. How is the technology affecting the fintech industry and helping it to grow? However, there are advantages and limitations of technology in the fintech industry.
Topic 4: In this section, know the potential of future growth in the fintech industry. What opportunities and challenges do companies face while adopting the fintech industry?
Topic 5: As you all know, app development is the most popular area with growth in technology. So, the fintech industry has also developed various apps that help customers understand the fintech industry and use it for payments and investments.
Topic 6: Still, many people need to know which app ideas would be best for their organizations. In this topic, you would know various thoughts to help you create and grow the app.
Topic 7: You will learn combining third-party services with fintech applications may have a lot of advantages but also present several difficulties that must be appropriately evaluated and handled.
Topic 8: You will know the cost estimation of fintech apps in various sectors.
Explanation of how fintech has evolved, from the earliest forms of electronic payment to the current state of the industry
Fintech may be divided into several distinct periods, following a study by Arneris, Barberis, and Ross. Each of these three (and a half) periods saw unprecedented market differentiation, which changed how customers interacted with their money. Let's examine the following periods:
Fintech 1.0 (1886–1967)
The infrastructure needed to enable globalized financial services is being built during this phase. The first transatlantic cable (1866) and Fedwire (1918) in the USA made it feasible for the first electronic money transfer system, which utilized telegraph and Morse code technology. Even if it was straightforward by today's standards, the advent of infrastructure and transportation marked a revolution in the ability to carry out financial transactions across longer distances.
Fintech 2.0 (1967–2008)
This era, characterized by the transition of finances from analog to digital, began with Barclays' launch of the first ATM in 1967. The Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunications (SWIFT), a method allowing financial institutions to interact with one another and enable a significant number of international transactions, and NASDAQ, the first computerized stock exchange in the world, were both established in the 1970s. The development of bank mainframe computers (and a "Gordon Gecko" sense of Wall Street style...) and the rise of Internet banking in the 1980s marked the continuance of this period and altered how individuals did business and saw financial institutions. When connected individuals started managing their money differently in the 1990s, the first steps toward digital banking were made. When PayPal was first created in 1998, it served as a precursor to the new payment technologies that emerged as society's reliance on the Internet increased.
The economy seemed to be doing well, and Gordon Brown, the U.K.'s then-chancellor, even declared the "end of boom and bust." However, this specific bust – the global This fintech era ended with the financial crisis of 2008, which also sparked the innovation that would define the one that followed.
Fintech 3.0 (since 2008)
New suppliers now have easier access to the market because of the financial crisis's impact on bank confidence and legislative change. 2009 saw the creation of Bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency built on a blockchain.
As more individuals use smartphones, mobile devices are increasingly used to access the Internet and other financial services.
The startup age has arrived, spurred on by customers' and investors' need for creativity in new goods and services. The shift away from the established banks of the Fintech 2.0 period has been the distinguishing feature of Fintech 3.0. Even established banks are beginning to operate and advertise themselves like startups.
New technologies have emerged to facilitate the development of digital banking products utilizing Open Banking, which grants access to financial data to outside organizations.
With the help of platforms for banking as a service (BaaS), like Treezor and SolarisBank, banks and other financial institutions may more easily abandon their cumbersome legacy systems and launch "neo-banks"—digital banks that have been created to improve customer experience.
3.5 Fintech
Someone put a cable beneath the Atlantic in 1886, which marked the beginning of Fintech 1.0 and how banks do business today. The preceding fintech periods only went a little further than that wire beneath the ocean regarding geography, with the bulk of development occurring in the industrialized world, namely in Europe and the USA.
We need to consider changes in consumer behavior and the availability of the Internet.in the developing world, and fintech 3.5 has been established. China and India, the nations that use fintech the most, are the furthest away from this cable. These nations can accept new ideas more rapidly than their Western counterparts because they are kept from the physical banking infrastructure that the West has.
Fintech 3.5 represents a shift away from the financial industry controlled by the West and recognizes global advancements in digital banking.
The Future
It's challenging to peer into a crystal ball and forecast the future since the globe is now recuperating from a severe epidemic. Venture Capital fintech financing decreased by $6.1 billion as of May 2020, reaching its lowest level since the first quarter of 2019.
Blockchain and open banking, the underlying technologies that propelled the Fintech 3.5/3.5 era, will continue to drive innovation in the future.
To strengthen customer relationships by creating a "segment of one," machine learning is expected to change how we interact with banks and insurance companies. Financial institutions can target individuals with specialized offers and support tailored to their needs, providing a more relevant experience.
While its competitor Revolut is building a machine learning tool to assist consumers budget based on their past 3-6 months of spending, German digital bank N26 is already providing customized deals, such as discounts with flexible workspace WeWork and online trip booking site GetYourGuide.
This development is not merely applied to the financial industry. Insurance companies will use machine learning to speed up insurance claims handling. The insurance company Ping An has created a method that automatically settles claims by employing an algorithm to identify the kind of car and the level of the damage before submitting an offer to pay the share right away. This is already happening in China.
According to several sources, the fintech business has reported tremendous development and change in recent years. Here are a few current trends in the fintech industry:
Fintech Startup Investments
Despite a minor decline in levels of investment during the first half of 2022, overall fintech investment levels are still quite strong. Global investments in fintech totaled $210 billion in 5,684 transactions in 2021. The top three regions for fintech investment were the Americas, EMEA, and Asia Pacific. However, owing to investors being more selective in their investments and raising the bar for fintech, only a little of this money goes to early-stage businesses.
M&A Activity
The value of M&A deals increased in the first half of 2022, rising by 52% to $46.4 billion from $30.6 billion in the first half of 2021. But the number of transactions dropped by 12% to 110. This may be indicated that more prominent players in the sector are interested in buying smaller fintech firms.
Launches of New Products
Businesses from all sectors are integrating pre-built financial solutions offered via current APIs into their software. The market for embeddable fintech is expanding quickly; it is anticipated to generate about $230 billion in revenue in the U.S. alone by 2025, up from $22.5 billion in 2020. This enables software businesses to provide services directly via their digital platforms –such as loans and payments- instead of developing the infrastructure. Digital payments, online loans, and robo-advisors are examples of newly released products.
Blockchain and Virtual Wallets:
Blockchain will take center stage in finance, increasing virtual wallets' capabilities. If national standards, security, and laws are in place, countries will be pleased to accept the technology.
The financial business is expanding and changing, creating new possibilities and difficulties for investors, established companies, and startups. Although funding is still robust, investors are becoming more selective and raising the bar for fintech businesses. Additionally, M&A activity is increasing, and new product introductions like digital wallets driven by blockchain technology and embedded fintech solutions are changing the economic environment.
Statistics on fintech funding and investment trends, including the total global investment in fintech, the top fintech investors, and the most funded fintech categories
Consumer Behavior
Financial technology businesses first caused adjustments in customers' expectations. With its reduced costs and charges, quicker services, and more accessibility, fintech businesses were even more alluring after the 2008 financial crisis, when consumers lost faith in traditional financial institutions.
Customers are now transforming the financial sector via their expectations, signaling a revolution in the business. Over the past ten years, people have become used to better customer experiences and all-around conveniences, such as personalized offers and same-day retail delivery. The typical banking consumer anticipates similar behavior from the financial industry. Additionally, Fintechs are adequate and better equipped to satisfy client requirements than conventional banks.
Additionally, Covid-19 sped up the implementation of fintech. According to the Swiss Finance Institute, during pandemic lockdowns, download rates for fintech apps rose from 29.2% to 32.8%. Even cautious clients flocked to fintech to manage their funds since traditional banks needed to be equipped to handle most banking activities remotely.
Advancements in Technology
Technology is mostly to blame for the rise of fintech. It has completely changed how financial services work, making them nearly unrecognizable from a decade ago since it functions almost purely in the virtual world. Fintechs are superior to conventional financial institutions in several ways because technology has enabled us to automate tasks that people previously did.
More efficient – Automation speeds up mundane processes and gives staff members more time to work on complex projects like strategy and innovation. Productivity has grown as a consequence.
Everyone has direct access to services and information since fintech has eliminated intermediaries like brokers and bank managers by providing various financial services online and via applications.
Fintechs could recruit fewer people while maintaining a very high level of productivity because of technology, enabling them to avoid paying for physical offices. Fintech solutions may appeal to a broad audience by offering lower service prices due to personnel and local branch cost savings.
Regulations
Generally speaking, rules might make it harder to be an entrepreneur. Although the financial technology sector is subject to regulatory requirements, many are less stringent than fully licensed banks' standards. As a result, financial technology firms may provide new financial products more quickly.
Additionally, a lot of countries actively promote digital banking. For instance, the U.K. Competition and Markets Authority mandated in 2016 that nine of the nation's top banks provide authorized startups access to their transaction data. This paved the path for more fintech companies to emerge and provide users with new options for managing their smartphone accounts.
The U.K. dominates the global fintech business, accounting for around 10%. The nation, though, doesn't take its success for granted. The U.K.'s Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) replaced its outdated Gabriel reporting system with Regdata. This new platform is more flexible and simplifies data submission to lessen the load of regulatory reports for fintech.
Using technology to enhance and automate financial services is known as fintech or financial technology. Fintech enterprises use a range of technology to upend conventional financial services and provide consumers and businesses with more effective, accessible, and user-friendly solutions.
Machine learning and artificial intelligence (A.I.) are two technologies that are employed in finance. TO automate procedures and provide more precise predictions, A.I. and machine learning may be applied. Additionally, they may be utilized to raise the effectiveness and precision of financial services. For instance, AI-powered financial advice may tailor investors' recommendations based on their investment objectives, risk tolerance, and other considerations.
Cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology are two more areas where fintech is evolving. By enabling safe and transparent transactions, blockchain technology has the potential to transform the financial sector completely. Cryptocurrencies can upend established payment systems and act as a means of exchange. To fulfill the demands of businesses and consumers, fintech firms are launching new cryptocurrencies and building new blockchain applications.
Another critical aspect of fintech innovation is mobile technologies. Mobile banking applications and Internet payment systems have significantly impacted how individuals send and receive money. Additionally, fintech firms extend services like mobile banking and peer-to-peer payment platforms while creating new payment technologies. Thanks to this, consumers may now more quickly and conveniently access financial assistance on the road.
Fintech firms have used technology to enhance several elements of their operations, including customer experience, cost savings, operational effectiveness, and safety. Here are a few instances:
Customer Experience
Mobile applications: Customers can access their accounts, conduct transactions, and manage their money while moving, thanks to the mobile apps that fintech business has created. Customers now have easier access to banking thanks to this.
Chatbots: Fintech businesses that offer customer support and address common queries have also adopted chatbots. The demand for human customer support personnel has decreased, and response times have improved.
Personalization: Companies aim to tailor their services and products to meet individual consumers' needs better. Fintech businesses have used machine learning algorithms. Customer loyalty and satisfaction have increased as a result.
Cost-Saving Measures
Automation: Many operations fintech businesses use, including risk management, fraud detection, and load approvals, have been automated. As a result, less physical labor is required, lowering expenses.
Cloud Computing: Fintech business has moved their infrastructure and data to the cloud to save costs on hardware and upkeep.
Efficiency:
Blockchain: Fintech companies have utilized blockchain technology to enhance the security and reliability of their transactions. Blockchain eliminates the need for intermediaries and enables quicker, more secure transactions.
API Integration:
Fintech companies have integrated APIs into their systems to facilitate seamless data exchange and service communication. Fintech companies have integrated APIs into their systems to facilitate seamless data exchange and service communication. This has increased effectiveness and decreased mistakes.
Security:
Biometric Authentication: Fintech companies have boosted their service security measures by implementing biometric authentication methods such as facial recognition and fingerprint scanning. Fraud and identity theft have decreased as a result of this.
Encryption: Strong encryption techniques have also been employed by fintech organizations to safeguard consumer data transactional information from online dangers. The overall security of their services has increased as a result.
Statistics on the use of fintech technologies, including the most widely used technologies and their rates of adoption

By providing creative solutions that are more accessible and efficient than conventional banking systems, fintech technology has wholly transformed the financial sector. However, it also poses several difficulties, such as:
Cybersecurity Risks
Since fintech businesses handle private financial data, hackers often target them. Data breaches, ransomware attacks, and phishing scams are examples of cybersecurity dangers. To protect their systems and clients' data, fintech businesses need to invest heavily in cybersecurity measures.
Issues with Security and User Privacy
With significant Fintech investments, the usage of financial technology in Europe expanded by 72% in 2020. New security worries are the most considerable unforeseen outcomes accompanying such an upgrade. Every 39 seconds, a recent cyberattack occurs, indicating that crime is increasing. Sadly, one of the most popular targets for hackers is the fintech industry.
People manage digital money more often today, so it shouldn't be surprising that fintech businesses have more sensitive data to secure than before. Because of this, even influential, respected organizations like top Forex brokers and national credit bureaus may have data breaches. In August 2020, the client data of Pepperstone, a well-known Australian brokerage, was hacked.
Potential for Established Financial Systems to be Disrupted
Fintech businesses are reshaping traditional financial systems by presenting fresh, cutting-edge alternatives. This disruption may threaten conventional financial institutions because they need help keeping up with the innovation rate. To achieve a seamless transition and reduce disruption, fintech startups must work with traditional financial institutions.
Overview of key areas of growth in fintech, including digital banking, payment processing, lending, insurance, and wealth management
The fintech industry has increased in recent years, and many important factors have contributed to its growth:
Digital Banking: The emergence of digital banking has completely changed how individuals access and manage their money. Checking and savings accounts, loans, and investment possibilities are just a few of the services digital banks provide, all of which may be accessed through a mobile app or website. As a result, access to banking services is limited.
Payment processing: Fintech has also advanced significantly in the payment processing industry. Thanks to organizations like PayPal, Stripe, and Square, businesses can now take payments online more quickly. In contrast, mobile payment applications like Venmo and Cash App have made sending and receiving money easier.
Lending: By providing loans to individuals and small companies with cheaper interest rates and more flexible repayment periods than conventional banks, fintech lending platforms like LendingClub and Prosper have disrupted the traditional lending market. People now find it simpler to acquire loans, especially those who may have been turned down by conventional lenders.
Insurance: Insurtech firms have employed technology to improve the accessibility and efficiency of the insurance market. Consumers can now acquire and maintain insurance plans more easily thanks to businesses like Lemonade and Metromile, which also use data analytics to provide more individualized coverage and pricing.
The Pandemic's Unanticipated Benefit: A Digital Adoption Boom
The COVID-19 epidemic has inevitably resulted in a rise in the use of digital technology. Consumers have not only dabbled in the internet world but have also plunged into incorporating it into their daily lives (via digital payment, investing technology, online-only insurance, etc.). The adoption goes beyond only the consumer market. MSMEs-micro, small, and medium-sized businesses –are using more fintech services. These companies comprise a separate client category with demands different from those of individuals and big organizations. India's digital economy is anticipated to increase exponentially to $800 billion by 2030 due to the expansion of UPI, digital public infrastructure, and the COVID-19 epidemic.
Horizontal Expansion: Filling the Profitability Gap in PayTech
In addition to supporting the rise of digital payments, the dynamic and fast development of the payments ecosystem, supported by the growing acceptance of technology and innovation, also promotes the availability of a variety of safe, secure, cutting-edge, and effective payment systems.
Neobank: Hyper-Personalized Goods Drive Collaborations
Neobanking platforms have grown steadily in quantity, as have international investments during the last several years. The Indian fintech sector has adopted a similar strategy, and the number of new banking firms in the nation is increasing monthly and luring foreign investors to this market. The ongoing financing received since 2017 is evidence of the growing interest in this industry. The epidemic, however, gave the financial activities a boost. Investors knew the potential neo-banks had for the broader financial services sector.
Ecological Banking: Unlocking Ecological Value
Ecosystem banking assists banks in India in enhancing the customer experience and producing long-term value for clients. Customers who previously relied on complicated and disjointed procedures across several apps managed by partners are now offered a single solution through ecosystem banking. Banks were forced to use a purchase or joint venture strategy to expand new services due to monolithic technical applications' high costs and complexity.
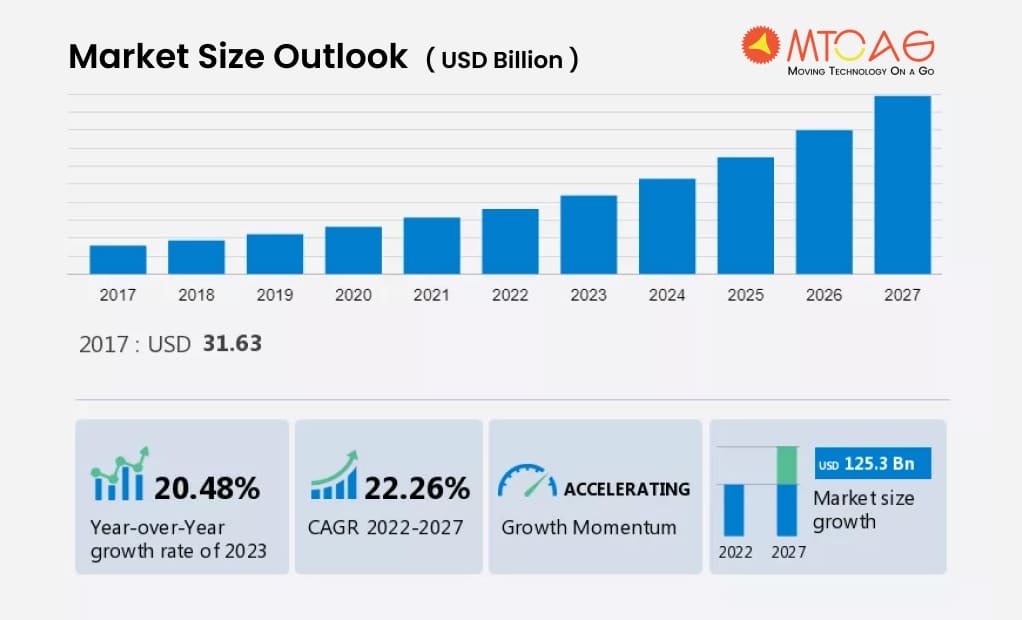
Statistics on fintech growth projections, including the projected market size of the fintech industry and the most promising fintech markets

Financial technology, or fintech, has expanded quickly in recent years, but several possible roadblocks might prevent it from developing further. Some of the most significant difficulties are as follows:
Regulatory Obstacles: Fintech businesses must deal with a complicated web of rules that might vary by jurisdiction and are frequently updated. This may make it challenging and expensive to adhere to all applicable laws and norms, which may impede innovation and make it more difficult for new players to join the market.
Talent Shortages: Because the fintech industry is so specialized, it calls for a distinct mix of abilities, including knowledge of finance, technology, and data analysis. Because of this, there is often fierce rivalry for the finest staff, which may make it challenging for smaller firms to recruit and retain the best workers.
Competition from Existing Financial Institutions: Due to the significant investments made by central banks and financial institutions in their fintech projects, it may be more difficult for smaller firms to compete. It may be difficult for new entrants to acquire momentum since these established competitors often have more excellent finances, resources, and well-known brands.
Fintech businesses must adopt an innovative and creative strategy to meet these issues. Several such tactics are as follows:
The accelerating speed of technological development has significantly impacted the fintech industry. To enhance their products' usability and user experience, I.T. consulting firms are looking into cutting-edge technologies like blockchain, IoT, and augmented reality.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology provides improved security and transparency, which makes it the ideal choice for fintech applications that deal with private financial data. IoT devices provide real-time data and insights experience for banking applications that need high user involvement.
The Growing Role of A.I. and Data Analytics in Fintech
Fintech applications are using data analytics and A.I. more and more to provide customized financial services. Fintech app development services may use data analytics to collect and analyze user data to understand better users' preferences, behaviors, and economic demands. This information may be utilized to provide specialized product recommendations, unique investment portfolios, and specialized financial guidance.
Contrarily, A.I. may automate standard financial processes like budgeting, saving, and investing, giving consumers more time to concentrate on more difficult financial choices. Consequently, fintech applications are improving their ability to meet the financial demands of their customers.
Fintech App Personalization and Customization
In finance applications, customization and personalization are becoming vital. Users anticipate that financial apps will be personalized to meet their unique needs and tastes.
Companies that create fintech apps use data analytics and A.I. to provide individualized financial services catered to each user's requirements.
Personalized investment portfolios, specialized product suggestions, and specialized financial counseling are just a few examples of how personalization may take place. On the other hand, customization enables users to personalize their usage of fintech apps by picking their preferred interface, establishing financial objectives, and choosing their preferred investing techniques.
Numerous advantages have resulted from the Fintech app development, including more accessible access to banking services and improved financial benefits. For Fintech firms to succeed in the sector, it offers several obstacles.
Increased competition is one of the biggest obstacles to developing Fintech applications. More businesses are joining the market as the Fintech sector expands, which may make it challenging for new entrants to distinguish. Building a compelling value offer, partnering for talent execution, and recruiting for potential rather than experience are all ways that fintech organizations may set themselves apart. Furthermore, a solid customer acquisition plan should be in place. This strategy should include partner ecosystems and unique methods for targeting and configuring each client category.
Regulatory ambiguity is another issue that Fintech businesses must deal with. Due to the sensitive information that Fintech businesses manage, they must abide by several laws, including data protection, anti-money laundering, and tax compliance [1]. Fintech businesses may find it challenging to manage these restrictions since they may be complicated and differ from one jurisdiction to another. Fintech companies should be prepared to negotiate with local and regional authorities to comply with regulations.
Finding investors and obtaining money are additional challenges in creating Fintech apps. Suppose fintech startups want to acquire financing backing in 2023. In that case, they must convince prospective investors of their attractive business plans and demonstrate why they are more likely to succeed than their numerous rivals. Fintech firms may also need help due to rising interest rates and the cost of funding.
One of the possibilities that result from these difficulties is that Fintech businesses must develop and modify their offers as necessary. Fintech businesses must be adaptable and ready to innovate in response to shifting consumer demands to remain ahead of the competition. This innovation may result in the creation of brand-new goods and services that will help the sector thrive.
In conclusion, developing Fintech apps is difficult because of the growing competition, regulatory uncertainty, and the need to acquire money from investors. Fintech businesses may overcome these obstacles by standing out from the competition, adhering to rules, and being adaptable and creative. By doing this, Fintech businesses may prosper in the sector and stimulate the expansion of the Fintech sector.
Paypal
You may send and receive money from friends and family using the payment app PayPal. Additionally, it may be used to pay bills and make purchases online. Buyer and seller protection are among the security measures that PayPal provides.
Venmo
You may send and receive money from friends and family using the payment app Venmo. You may also share expenditures and invoices with other users. The social feed feature of Venmo lets you see what your friends are purchasing.
Robinhood
Trading without commissions is available via the investment app Robinhood. It lets you purchase and trade cryptocurrencies, ETFs, options, and equities. To further your knowledge investing, Robinhood also provides a variety of instructional materials.
E-wallet
Plastic money was developed when it became clear how difficult carrying cash was. However, the advent of e-wallet applications over the last several years has also signaled the end of plastic money. E-wallets are widely used and have a sizable market.
The market for e-wallets was estimated to be worth around $16.65 billion in 2013; by 2019, it had grown to an incredible $2,043.1 billion, and by 2027, it was expected to reach $7,580.1 billion.
This steep growth has also increased the need for e-wallet app development services. People utilize these applications for various reasons, including the substantial rewards they provide on every transaction made via these e-wallets, such as gift vouchers, cashback, and other discounts.
Exchanging Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrency has gained popularity in the financial industry over the last few years and is currently regarded as one of the best fintech app ideas for companies. Numerous other cryptocurrencies, including Dogecoin, Ethereum, and many more, have increased significantly in value as a result of the popularity of Bitcoin.
Some applications on the market provide real-time pricing of various currencies for trading cryptocurrencies. Additionally, these applications provide updates, news, and recommendations to assist you in making money while trading. Fiat currency is utilized in this context for all exchanges.
You may trade in these cryptocurrencies in the comfort of your home with complete transparency and the security of your money. In a short amount of time, several of the top cryptocurrency trading applications, such as Coinbase, Binance, etc., have become well-known internationally. As a result, creating a Bitcoin exchange platform is one of the best ideas for a financial app to create a successful fintech firm.
Explanations of key features that can help make a fintech app successful, including user interface, security, and integration with other financial services
Finance organizations can attract new customers and retain current ones by investing in a mobile app equivalent for their services.
There are a few things you should think about to create an app that will succeed if you find yourself in this business and require one as well.
Usability and an Intuitive User Interface.
For finance applications, usability is crucial. Fintech applications must be simple to use and navigate since they are utilized on mobile devices rather than conventional banking, which requires clients to visit a physical facility. Customers will rapidly lose interest and go to another app if an app is challenging to use.
Clear and straightforward directions, easily accessible buttons and menus, and a logical structure are all characteristics of good usability. Customers don't have to figure out how to use a fintech app since it is beautifully designed, making it simple for them to accomplish what they want to do.
Customer Data Protection Security Aspects.
Another major priority for finance applications is security. Customers need to feel confident about entrusting their financial information to these applications. Password encryption, fraud prevention, and data protection should all be security measures.
Integration with Other Services and Financial Applications.
Most fintech applications are designed to integrate with other financial services and apps. This makes it simple for clients to transfer money across their various accounts.
Additionally, it makes it simpler for clients to utilize several services from the same vendor.
Customer Assistance.
Even the finest fintech applications sometimes have issues that need to be resolved. So that customers may access assistance when required, applications must have a customer support structure in place.
Contact with customers may be via phone, email, or online chat.
Statistics on the most popular features of fintech apps and their adoption rates

A website or application must have an excellent design to be aesthetically pleasing and user-friendly. To keep in mind while designing, remember the following:
Navigation:
Layout:
Typography:
Explanation of the regulatory requirements for fintech apps, including data privacy and security
Enhanced Code Security
Since your application's code is its foundation, security should start there. Here are some tried-and-true strategies for guaranteeing your code's reliable performance right away:
By default, deny. Ensure all the app's control features and security are protected from outsiders and accessible as needed.
Access control policy. Only authenticated and authorized users should be allowed access; suspect I.D.s, unauthorized parties, etc., should be denied.
Use the messaging settings in the framework. Framework messaging may assist in building a solid code structure based on ready-made templates with a respectable security level throughout the development process.
Safeguard the app's SQL. Use various penetration testing techniques to check your application for vulnerabilities.
explanation of the benefits and challenges associated with integrating fintech apps with third-party services, such as banks and payment processors
Integrating fintech applications with third-party services like banks and payment processors has advantages and disadvantages. Let's examine each in more detail:
Benefits:
Challenges:
The prices for developing popular app categories, including banking apps, loan apps, investment apps, personal finance apps, and insurance applications, are shown below.
Development Cost for Different Apps (Approx.)
Fintech Industry has been the most significant part of the technology sector. With the help of this industry, payments are made easily with just a few clicks. So, in this blog, you will know the complete information about fintech, from its history to the future with apps and technology.